excellent doc:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/configuration.html#configuring-networking
==================
used raspberri pi imager to configure the SD card set a username and pwd, enable SSH
======================
si non detecté, relancer avec le desktop (brancher ecran micro HDMI et clavier usb) démarrer sur CLI
enable I2C
excellent tuto :
https://www.abelectronics.co.uk/kb/article/1/i2c-part-2-enabling-i2c-on-the-raspberry-pi
utiliser cmdr comme shell, bien installé!
what is my raspi's IP?
j'ai utilisé nmap
pour rechercher les appareils connectés et leur IP
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
By using the -sn flag, we are telling the nmap tool to ping every address on that subnet but do not scan for open ports.
pour détecter les équipements i2C connectés
$ sudo i2cdetect -y 1
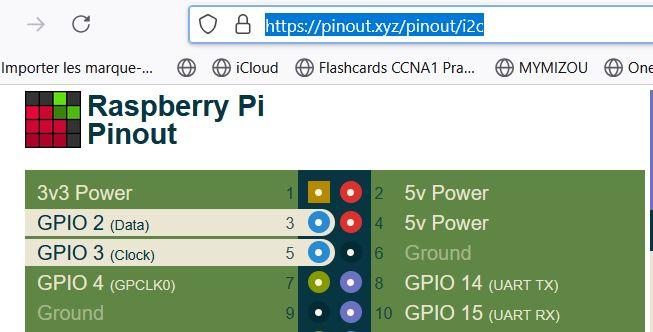
pour pins physiques:
https://pinout.xyz/pinout/i2c
TMP 117:
- connect 3V power GPIO 1
- connect GND to GPIO 9
- Connect board SDA (blue wire) to GPIO 3
- Connect board SCL (yellow wire) to GPIO 5
Vérifie que le module I2C est bien chargé :
ss
lancer jupyter notebook sur raspi:
jupyter notebook –no-browser –ip=0.0.0.0 –port=8888
code : voir jupyter notebook
sqlite3 : gestion de la table temperature_data
sqlite3 temperature_data.db
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM temperature_data;
import smbus2
import time
I2C_BUS = 1
TMP117_ADDR = 0x48
TEMP_REG = 0x00
def read_temperature():
try:
bus = smbus2.SMBus(I2C_BUS)
raw_data = bus.read_word_data(TMP117_ADDR, TEMP_REG)
# Inversion des octets (Little-Endian → Big-Endian)
raw_data = ((raw_data << 8) & 0xFF00) | ((raw_data >> 8) & 0x00FF)
# Gestion du complément à deux
if raw_data & 0x8000:
raw_data -= 1 << 16
# Conversion en °C
temperature = raw_data * 0.0078125
return round(temperature, 2)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Erreur lors de la lecture du capteur : {e}")
return None
finally:
bus.close()
# Boucle d'acquisition pour tester en continu
for i in range(10): # Lire 10 fois
temperature = read_temperature()
if temperature is not None:
print(f"Température: {temperature}°C")
time.sleep(2) # Pause de 2 secondes entre les mesures
Si la carte SD est presque pleine :
vérifier avec : df -h
Supprimer les paquets inutiles :
sudo apt autoremove
sudo apt clean
Vérifier les logs volumineux :
sudo journalctl –vacuum-time=2d
(Cela supprimera les logs plus anciens que 2 jours.)
Supprimer les fichiers inutiles dans /home/pi/ :
du -sh /home/pi/*